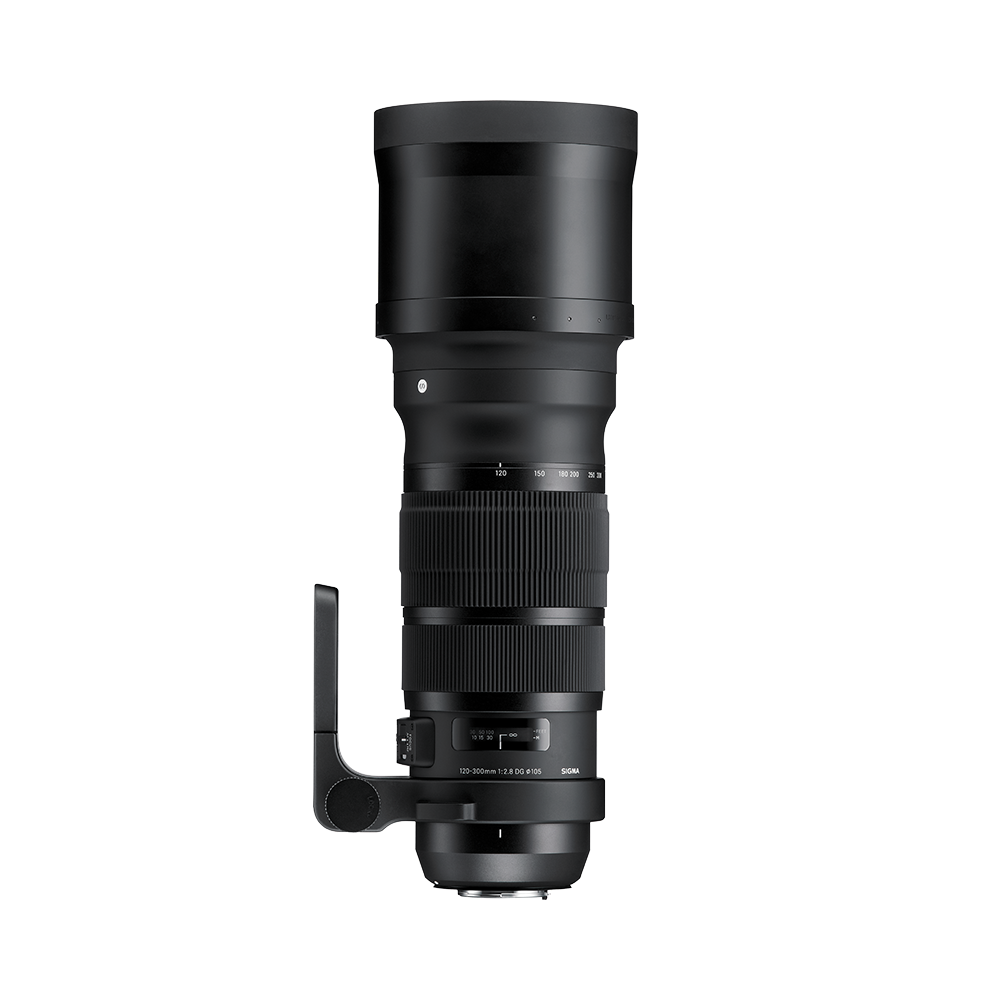
120-300mm F2.8
DG OS HSM
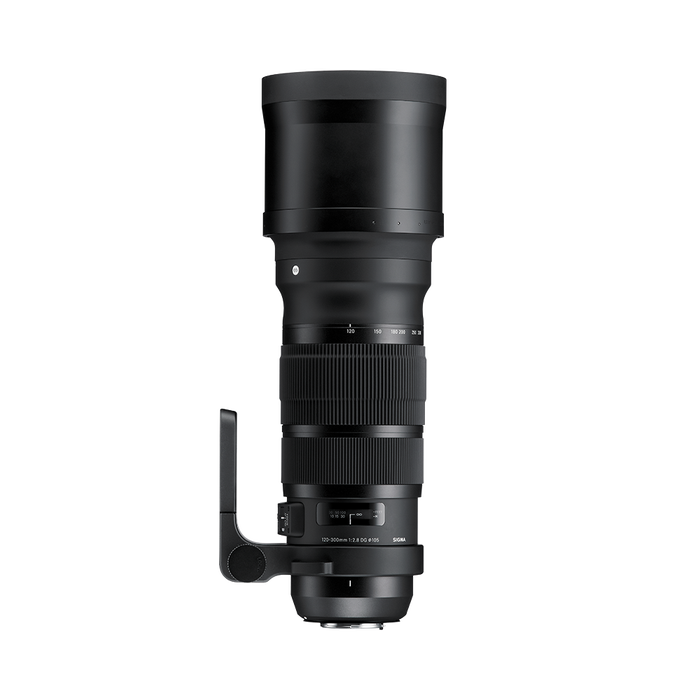

• Large aperture with great zoom range
• Includes technology such as a HSM & OS
• Accessories include: Lens Hood (LH1220-01) & Carrying Case.
| Angle of view | Telephoto | |
|---|---|---|
| Camera Type | DSLR | |
| Lens Mount | Canon EF-mount, Nikon F, Sigma SA | |
| Sensor Size | Full Frame | |
| Construction | 23 Elements in 18 Groups | |
| Angle of view | 20.4º - 8.2º | |
| Number of diaphragm blades | 9 (Ümardatud Diafragma) | |
| Minimum aperture | F22 | |
| Minimum focusing distance | 150 cm - 250 cm | |
| Maximum magnification ratio | 1:8.1 | |
| Filter diameter | 105mm | |
| Dimensions (diameter x length) | ⌀ 124.4 mm x 29 mm | |
| Dimensions (diameter x length) | ||
| Weight (g) | 3390 g | |
| Weight (g) | ||
| Edition number | S013 | |
| Supplied Accessories | Lens Hood LH1220-01, Front Cap LCF-105mm III, Rear Cap LCR II, Tripod Socket TS-51, Case LS-137K | |
| Accessories | WR Ceramic Protector Filter 105mm, WR Protector Filter 105mm, WR C-PL Filter 105mm, Tele Converter TC-1401, Tele Converter TC-2001, Mount Converter MC-11, Mount Converter MC-21 | |
| EAN | Canon E/EF 085126137540 |
|
| EAN | EAN | |
| Specifications Info | * The appearance, specifications, and the like of the product are subject to change for improvement without notice. DISCONTINUED MODEL |
|
LENS CONSTRUCTION
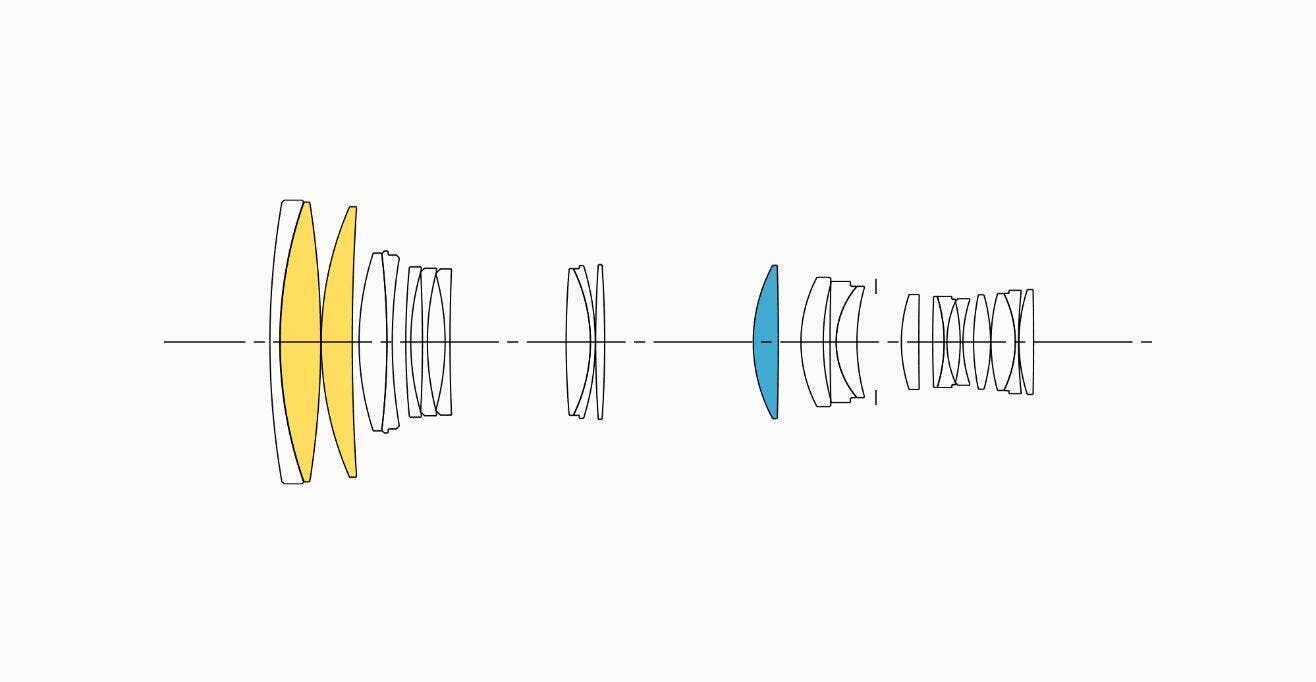

|
|
|
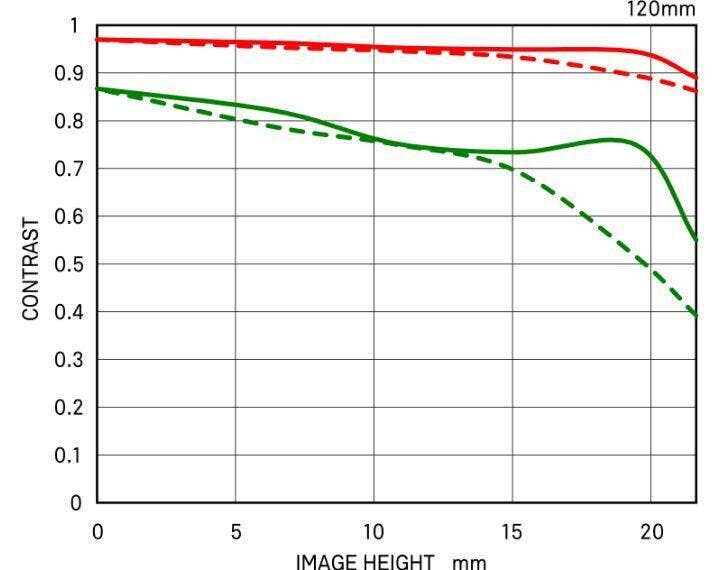
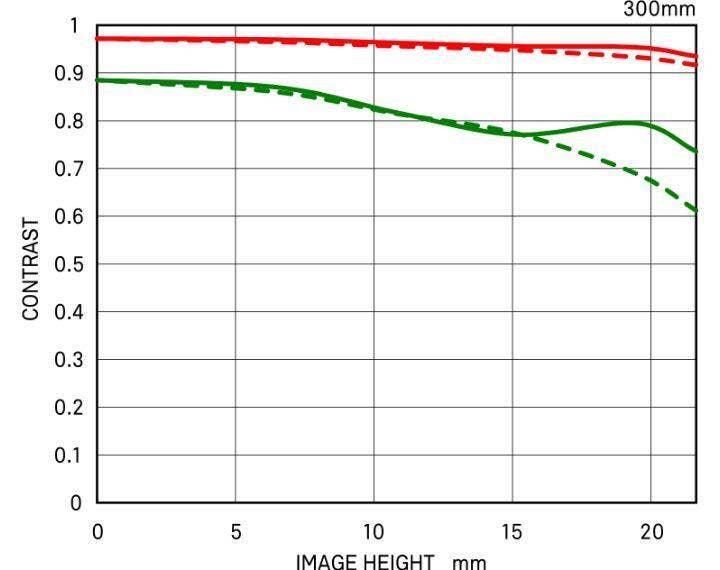
MTF CHART
There are two types of MTF chart. One considers the diffraction quality of light, which is called "Diffraction MTF", and the other, "Geometrical MTF" does not.
The quality of light appears in the diffracted light, and becomes more distinct as the F value gets bigger, resulting in lower image quality. Also, diffracted light exists at every aperture, which is why Sigma has been releasing Diffraction MTF data from the beginning since it is very close to the actual image data.
The advantage of using "Geometric MTF" data is that it is easy to measure and calculate since it does not consider the diffraction quality of light, yet it tends to show higher values in the graph than actual images.
The readings at 10 lines per millimeter measure the lens's contrast ability ( red lines), repeating fine parallel lines spaced at 30 lines per millimeter measure the lens's sharpness ability (green lines), when the aperture is wide open.
Fine repeating line sets are created parallel to a diagonal line running from corner to corner of the frame, are called Sagittal lines (S) and sets of repeating lines vertical to these lines are drawn, called Moridional (M) line sets.
*The MTF chart gives the result at the wide-open aperture.
|
Spatial frequency |
S:Sagittal Line |
M: Meridional Line |
|
10lp/mm |
|
|
|
30lp/mm |
|
|
DIFFRACTION MTF 120MM

DIFFRACTION MTF 300MM

GEOMETRICAL MTF xxxMM
Dust and Splash Resistant Structure
This lens features a highly effective dust and splash resistant structure with special sealing at the mount connection, manual focus ring, zoom ring, and cover connection.
*Although this construction allows the lens to be used in light rain, it is not the same as being waterproof, so please prevent large amounts of water from splashing on the lens. It is often impractical to repair the internal mechanism, lens elements and electric components if they are damaged by water.
High-precision, rugged brass bayonet mount
The brass mount combines high precision with rugged construction. Its treated surfaces and enhanced strength contribute to the exceptional durability of the lens.
Inner Zoom
The lens incorporates an inner zoom. With their unchanging barrel length, these lenses also enhance balance and stability for the photographer. Furthermore, since the front of the lens does not rotate, polarizing filters can be used with extra convenience.
HSM (Hyper Sonic Motor)
The Hyper Sonic Motor (HSM) is an original Sigma development that uses ultrasonic waves to drive the autofocus mechanism. Its extremely quiet operation helps avoid disturbing photographic subjects. High torque and speed assure rapid autofocus response. Sigma uses two types of HSM: ring HSM and micro HSM. The Ring HSM configuration permits manual fine tuning of focus (manual override) by turning the focusing ring after autofocus is complete.
Rounded diaphragm
The polygonal shape of a conventional iris dia phragm causes out-of-focus light points to appear polygonal. A rounded diaphragm is designed to pro duce rounded out-of-focus light points when opened to near maximum aperture. This creates attractive bokeh effects in many situations, such as when pho tographing a subject against an out-of-focus surface of water from which light is being reflected.
OS (Optical Stabilizer) function
Sigma's original OS (Optical Stabilizer) function uses sensors inside the lens to detect any motion, then moves specific lens elements in order to effectively minimize blur caused by such movement. Owing to the stabilized image in the viewfinder, it is possible to fine-tune composition and ensure accurate focusing.
Exclusive low-dispersion glass
The degree to which light is refracted by glass depends on the light's wavelength. This fact causes different colors of light to focus at slightly different points. The result is chromatic aberration, the color fringing that is particularly noticeable in telephoto lenses. Most chromatic aberration can be removed by combining a high-refractivity convex lens element with a low-refractivity concave element. Yet residual chromatic aberration known as "secondary spectrum" may still remain. To minimize this secondary spectrum, which can be a serious issue with conventional lenses, Sigma lenses feature up to three types of exclusive low-dispersion glass offering superior performance: ELD (Extraordinary Low Dispersion), SLD (Special Low Dispersion) and FLD ("F" Low Dispersion). In particular, FLD glass offers ultra-low dispersion in combination with high transmittance and the anomalous dispersion characteristics of fluorite. Meticulous deployment of these types of exclusive low-dispersion glass and optimization of power distribution gives Sigma lenses superlative image rendition undiminished by residual chromatic aberration.








